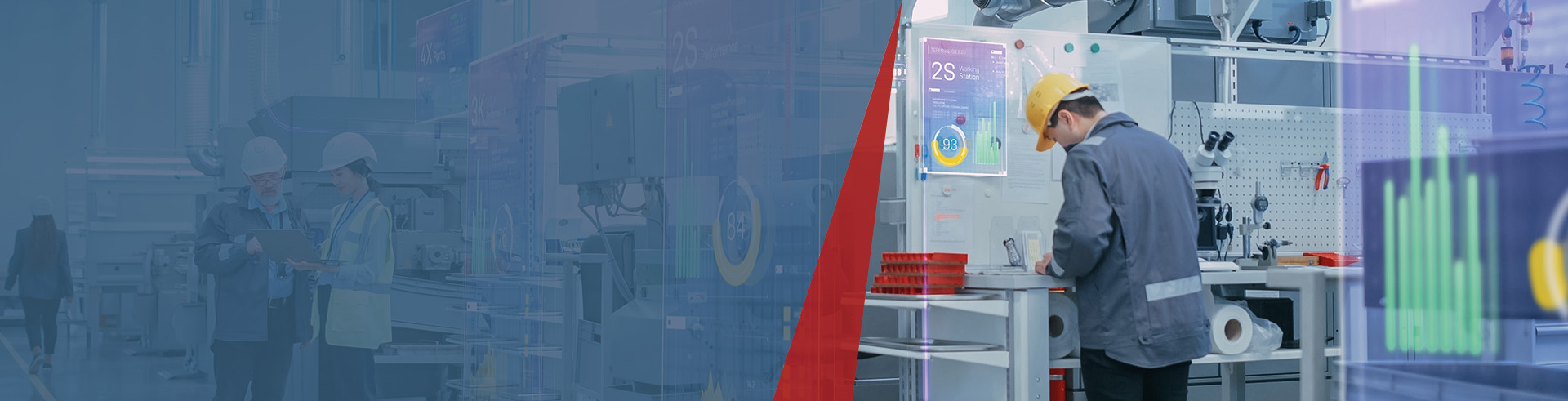
March 14, 2024 | Authors: Maren Fichtner & André Nimtz | Reading time: approx. 10 minutes
What does digitalization of production actually mean?
The term digitalization of production encompasses the use of networked, digital and automated technologies in manufacturing and production processes. It starts with the machines and processes and the resulting data.
But it also includes networking between different departments of a company as well as with suppliers, partners and customers. A key component is the end-to-end digital recording of data, its structuring and further processing.
The goals behind this are very clear:
- ensure and increase productivity and competitiveness
- enable efficiency and company growth
- increase resilience to global crises
The buzzwords behind the digitalization of production
Behind the actual process of digitalization in production, there is a whole range of buzzwords floating around. Have you already introduced the IIoT? What about your smart factory and your position in Industry 4.0?
But to be honest: you don't need to worry about these terms, because they stand for concepts that are intended to summarize the actual digitization processes.
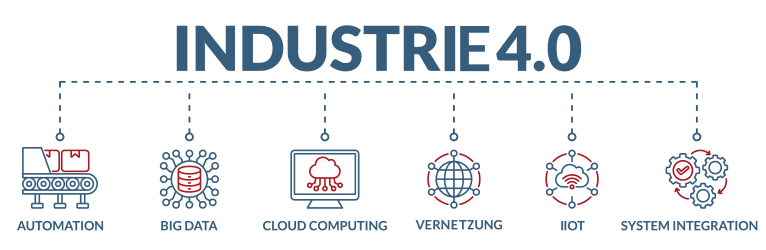
Industry 4.0
is often used as a synonym for digitalization and stands for the combination of automated, traditional industrial and manufacturing processes with intelligent technologies and networked talking machines. Traditional production facilities are being restructured in the course of Industry 4.0 thanks to modern technologies such as robotics, autonomous vehicles, etc.
Smart Factory
or translated "intelligent factory" is a central component of Industry 4.0 and refers to consistently transparent, intelligently networked and therefore agile production. Taken to the extreme, this creates a production environment that organizes itself without human intervention.
Industrial Internet of Things
refers to the networking of industrial systems and assets such as cameras, sensors, control units and also software solutions with modern internet technologies. The IIoT is, so to speak, the technological basis for the digitalization of all production processes.
Reasons for digitizing your production processes
"Our processes have grown historically and are correspondingly complex." Many companies have to approach the digitalization of their own production processes with this in mind. And that is completely normal.
Only very few companies can keep up with every technological disruption immediately. However, the wealth of challenges that manufacturing companies face today makes sustainable digitalization unavoidable. These challenges include:
![]()
uncertain supply chains & material shortages
![]()
rising costs for materials, personnel & energy
![]()
increasing individualization of products & solutions up to batch size 1
![]()
shorter delivery and response times
![]()
shortage of skilled workers
![]()
increasing requirements for sustainable production
![]()
regulatory obligations to provide evidence & compliance with standards
![]()
cybersecurity & data security
![]()
susceptibility to errors in manual processes
![]()
inefficient processes & lack of flexibility or responsiveness
Typical use cases for the digitalization of production
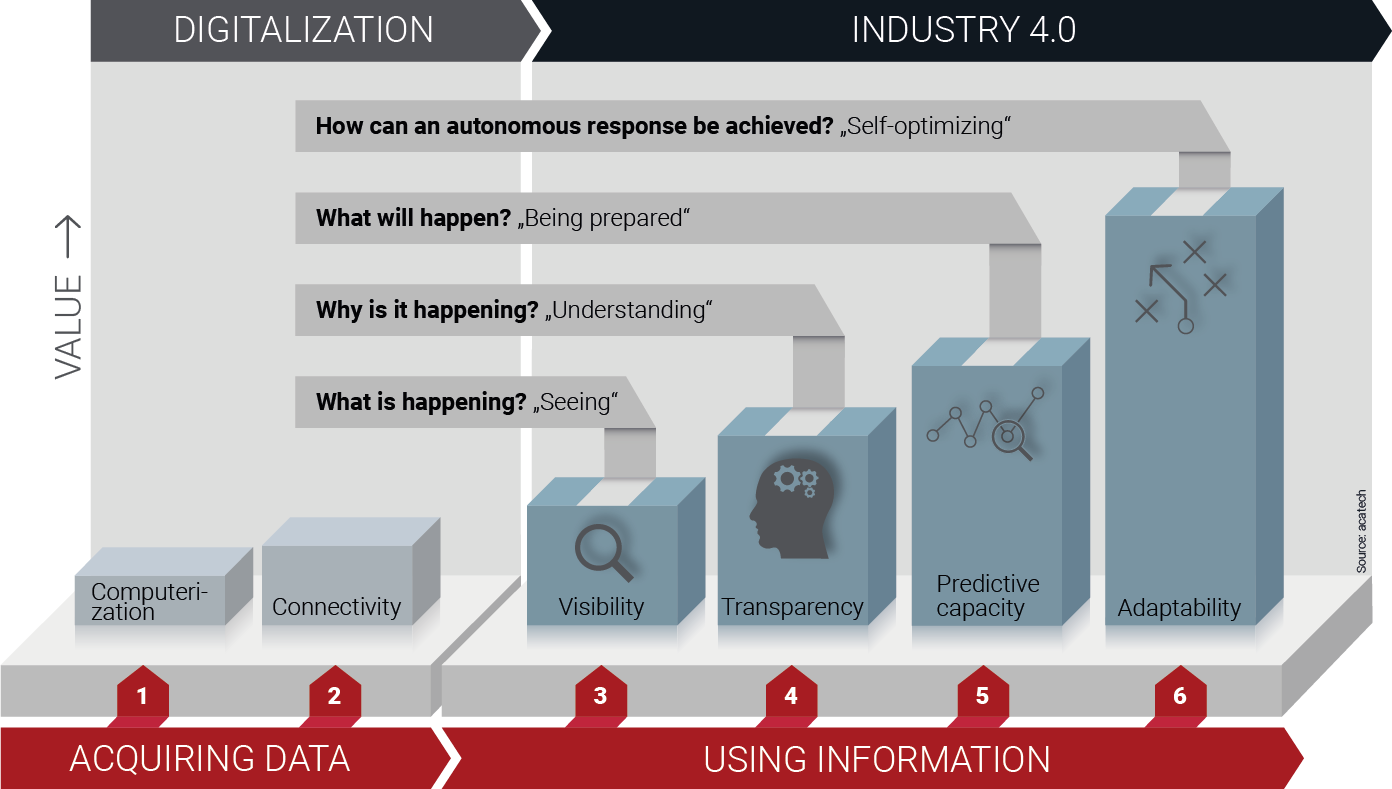
Imagine the digitalization of your production like the route plan in a navigation system: The destination is digitized production and you are somewhere on the blue line that leads past various stations.
How you tackle the first (or next) steps depends entirely on where you currently stand. At the very beginning of the digitalization roadmap is networking ...
Step 1: Connected production
What does that mean?
It starts with the networking of assets on the store floor and networking from the store floor to the top floor. In most cases, this involves networking from physical to digital (e.g. by retrofitting existing machines with sensors). However, digital to physical (e.g. through the control of cobots) or digital to digital (e.g. through self-controlling AI) are also scenarios.
Why?
Real-time data streams between sensors, peripheral systems, databases, etc. enable the continuous collection of production and process-relevant data. This forms the basis for all further digitalization steps.
Step 2: Big Data
What does that mean?
As soon as data can be collected, it is generated - quickly and in large and not necessarily comprehensible quantities. Digitalization creates concepts for handling this data.
Why?
Data must not only be collected, but also managed. Big data projects involve structured data collection, storage, processing and evaluation.
Step 3: Visualization of data
What does that mean?
Up to this point, data is still just data. However, people are visually oriented. Therefore, the next step is to visualize collected data in a user-focused way, for example in dashboards.
Why?
Properly visualized, data creates transparency about production processes and enables production optimization, e.g. through machine or condition monitoring.
Step 4: Digital twin
What does that mean?
In addition to your physical machines, you have access to an exact digital image of them. This in turn is continuously fed with live data.
Why?
The digital twin gives you the opportunity to carry out simulations and analyses in order to discover potential for improvement. The best thing about it: the real asset in your production remains unaffected the entire time.
Step 5: Data Analytics
What does that mean?
From this point onwards, you analyze large volumes of data and historical data to gain insights into production processes and identify trends. The prerequisite for this is historical data that has been collected systematically and in a structured manner over a longer period of time.
Why?
The analysis reveals patterns that enable production processes to be optimized.
Step 6: AI in production
What does that mean?
AI technologies such as deep learning are at the end of the digitization of your production processes and require a high degree of structured data collection and processing. However, if this data is available, you can take a huge step towards intelligent and sustainable production using AI.
Why?
AI-supported processes enable a significant increase in efficiency and flexibility in your production and help you to reach the right conclusions quickly. Machines make their own decisions based on historical data. Predictive maintenance and self-controlling systems are possible.
Side effects of the digitalization of production

The question of IT security and cybersecurity
The concept of digitalization is often associated with very conservative concerns: If you send all your data online, how secure is your production? Are you still protected from hackers and malware?
And we don't want to deceive you: The danger exists and must always be considered in digitization projects. However, digitalization comes with its own protection options that can be used to secure your production facilities. Determining your individual security situation and optimizing it should always be part of the digitalization process.

New business models towards product 4.0
In the course of digitalization, you make your data usable and exploitable - not only for yourself but also for your customers. This opens up opportunities for new, data-based business models.
An example: Until now, machine manufacturers sold their machines. After the machine was before the machine. In the future, machine manufacturers will be able to sell better support, optimized maintenance processes and digital machine services thanks to data collection using built-in sensors and other IIoT technologies. This creates added value for the customer and new and lasting sales potential for the machine manufacturer.

Work 4.0 or: the new role of people in production
And that brings us to the most serious objection: if everything is digitalized, why do we still need people? The answer is that they are just as necessary as before, but their role is changing.
People must be involved in the process of digitalization from the outset so that they can grow confidently into their new role. They must lose their fear of losing their job and at the same time adopt new processes and acquire knowledge. The digitalization of production processes then results in numerous advantages, such as
- process-reliable, software-supported execution of work steps
- faster training times and professional qualifications
- increased satisfaction and motivation thanks to modern digital workplaces
- cobots and robots take over heavy physical work
Beyond this, digitalization opens up completely new fields of work and aligns the company for New Work and Work 4.0. The next generations are growing up with new technologies and are particularly attractive to you as digital talents.
Digitalized production: obstacles, risks, opportunities
In order to seize the opportunities of digitalization, you will most likely also have to take risks. And you should also be aware of these for your company so that you can assess at what point which degree of digitization pays off.
We have compiled a series of obstacles, risks and opportunities for you:
Obstacles
- lack of financial resources
- data protection requirements (should software providers have access to my production and personnel data?)
- unclear IT security requirements (keyword: Cyber Resilience Act)
- lack of skilled workers
- complexity of the topic
- internal resistance from employees, e.g. due to concerns about their jobs
Risks
- high initial costs & lack of insight into ROI
- greater vulnerability to hacker attacks
- insufficient technology and interface standards
- incorrect assessment of priorities due to lack of digitalization experience
- technology dependencies / vendor lock-in
Opportunities
- creation of end-to-end information flows (IT and OT)
- data-based decisions for process optimization
- traceability of processes
- greater flexibility, transparency and efficiency
- reduction in costs (production, maintenance, commissioning, etc.)
- increase in product quality
- increase machine and system availability (zero downtime)
- better customer relationships thanks to greater individuality and shorter time-to-market
- strengthening your market position through new business models, digital services, etc.
6 steps for successful digitalization of production
When digitizing your production processes, the "how" is at least as important as the "what". The process must be focused on just as much as the solution. There is little chance that bad processes will lead to good solutions. Or as we like to say: "Bad processes digitized are still bad processes."
That's why we suggest a 6-step approach:
Step 1: Find a trustworthy digitalization partner
Work together with experts. In very few cases is there sufficient expertise in-house to evaluate the scope of digitization. You should therefore look for a partner who has the necessary experience, but who also has the right chemistry. You will be working together for quite some time and are dependent on mutual understanding.
Step 2: Maturity assessment along the maturity index
The first step is not implementation, but assessing where you stand and where the journey should take you. Your partner uses the maturity model, for example, to evaluate and advise you on what your actual and target status is.
Step 3: Identify profitable use cases (low hanging fruit)
Then it's time for the first project. This should never be the big answer to all digitization questions. Look for a project that can be brought to measurable success quickly. This will secure the status of your collaboration and also send a positive signal to your employees.
Step 4: Carefully planned roadmap and end-to-end digitalization strategy
In this step, you broaden your view of the big picture. You look at all processes end-to-end and identify potential problem areas. Draw up a roadmap and a digitalization strategy that focuses on holistic solutions. Isolated solutions and costs for unnecessary technologies are eliminated.
Step 5: Involve employees and stakeholders in the process
Once the overall goal is clear, the time has come to get your employees on board. After all, they should work with the solutions and feel comfortable doing so. This step is primarily about reducing internal resistance.
Step 6: Agile approach in sub-projects (sprints) instead of large projects
The concrete implementation is next. Do not set yourself project goals that are too big. Instead, work agilely from one sub-project to the next. This reduces the initial costs and allows feedback to be regularly incorporated into the ongoing process. You may not reach your goal tomorrow, but you will make sure that you actually get there.
iSAX brings digitalization to your production
In many cases, the digitalization of production processes is based on custom software development; "off-the-shelf" software rarely fits your use cases. This is why we have specialized in developing precisely such solutions. We help you to future-proof your company with the right software solutions.
You can rely on this with us
![]()
Support
We support you from the idea to the realization of concrete use cases and digital services.
![]()
Consulting & concept
We support you in the digital transformation of your company. Our services include:
- recording the current status and requirements
- definition of use cases and framework conditions
- implementation consulting and creation of a solution architecture
- technology selection and best practices
![]()
Implementation
We work with agile methods, modern technologies and common platforms and develop solutions with which you can
- gain data from your existing machines
- use information for specific IIoT scenarios
- support your workers in their workflows
Conclusion
The digitalization of production is more than just a buzzword and, above all, it is not an end in itself. On the contrary, it will unlock potential in your company without which your competitiveness will suffer. Despite all the risks and challenges, there are plenty of opportunities for your company's profitability in the digitalization of your production processes. To ensure that you achieve optimum results, you should look for a digitization partner with industry experience with whom you can communicate as equals.
Free webinar:
Practical examples around the digitalization of production

How are companies implementing the digitalization of production? How do they tackle specific use cases? And what are the long-term benefits of the solutions developed? In our free on-demand webinar, we will give you insights into the practice of production digitalization. Register now.