Definition: What is process reliability?
Process reliability describes how safe and reliable processes are. A high degree of process reliability means that a company can carry out its processes reliably and without disruption and can therefore meet its targets on time and in the right quantities.
Process reliability in production relies on a range of measures and systems to ensure that production processes are stable, reliable and do not endanger people, machines or products. Ideally, errors and malfunctions should not occur in the first place.
Incidentally, the term process reliability is often used as an alternative to the term process reliability. Process reliability is increasingly used in manufacturing, mechanical engineering or software development whenever the aim is to ensure stable, efficient and continuous processes.
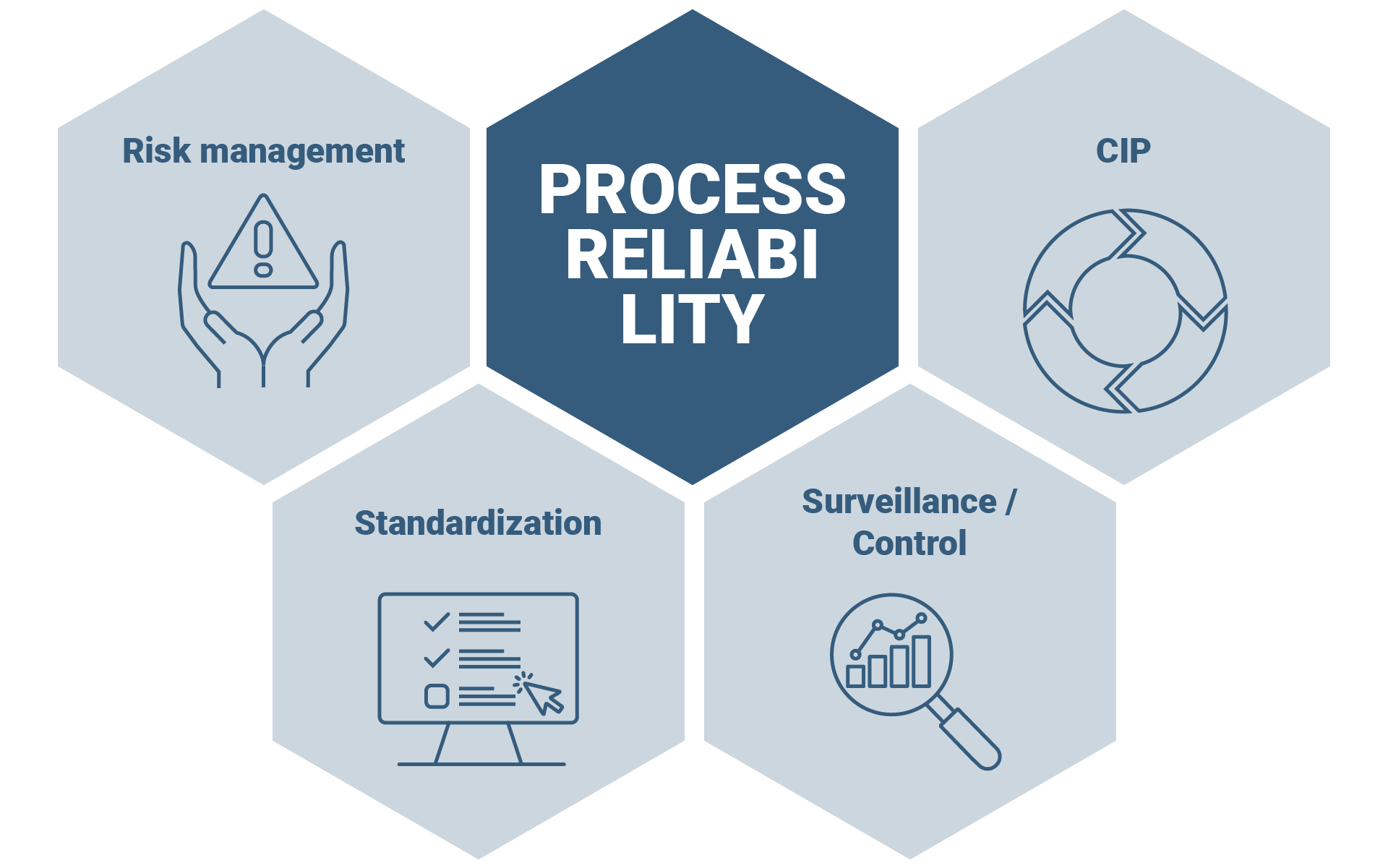
How to achieve a high level of process reliability?
Step 1: Risk management
The first step is to identify what could jeopardize the security of your processes. To do this, carry out a risk assessment and identify possible sources of error and weak points in your processes and workflows. Analyze past errors and malfunctions and identify their causes.
Step 2: Standardized workflows for greater process reliability
Once you have found your problem children, get to grips with them. This works best with standardized workflows. Standardized processes leave little room for deviations that could reduce process reliability.
Standardize your instructions and documentation processes. Provide your employees with detailed digital work instructions that guide them through the process step by step. Maintain and update your instructions in the system to reflect new requirements and changes and roll out adjustments in real time. The digital instructions can also document all steps.
Train and inform your employees - comprehensively and continuously. Promote the skills of your employees through practical training and system-inherent training. Ensure that your employees always have up-to-date knowledge of processes and their execution.
Step 3: Monitoring and control
Trust is good, control is essential. Especially when it comes to process reliability in your production. Record all conceivable data, evaluate it continuously and establish real-time monitoring where possible. Continuous monitoring of your production processes enables deviations to be detected at an early stage.
Supplement real-time monitoring with regular audits and check compliance with all safety and process standards based on defined criteria.
Step 4: Continuous improvements
Finally, establish continuous improvement processes. A process that is safe under today's conditions may fail tomorrow. Keep a watchful eye on your process reliability and optimize as soon as a need arises.
What are the advantages?
If you strive for process reliability, the optimization of your operating procedures is almost a matter of course, as you are concerned with eliminating errors and faults from your processes.
Of course, this ultimately results in an increase in product quality. Higher customer satisfaction can also be counted among the benefits of process reliability, as it enables you to meet production deadlines and schedules.
Another significant advantage is the minimization of potential risks - for your profitability, but above all for man and machine. Process reliability can prevent dangerous incidents and ensure a high level of safety for your employees, the environment and the infrastructure.
Can process reliability be measured?
Process reliability depends on many factors that can be difficult to measure. Process reliability, on the other hand, is somewhat more specific. You can actually measure this with the help of the reliability ratio.
Basically, the reliability ratio simply relates the number of good parts, for example, to the total number of units. An example calculation: You have produced 100 pieces, 96 of which are good parts. In this case, the reliability ratio is 0.96 or 96%. The higher this ratio is, the more reliable the process is.
What are the objectives of process reliability?
Process reliability is intended to ensure that production processes run smoothly and without disruption and to guarantee the continuity and quality of processes.
In this way, process reliability supports the fulfillment of your production targets in accordance with specifications.
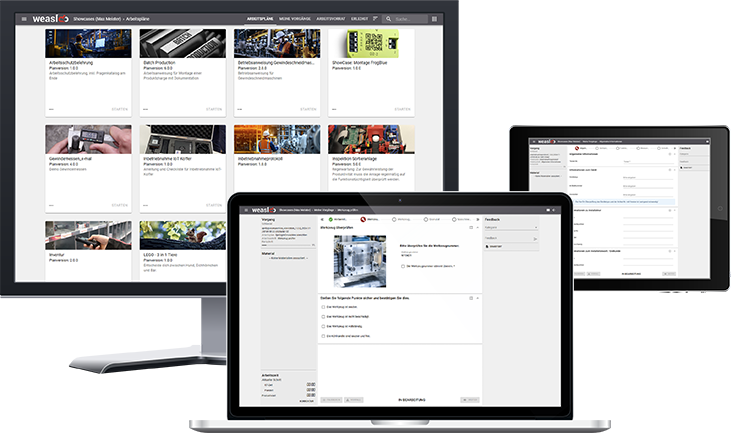
Reliable production with worker guidance
Standardized processes are an essential component of process reliability. And with a worker guidance system, you can easily establish such processes in your production and assembly.
With weasl, you can provide your employees with a tool that guides them through their orders with process reliability. You can experience how this works in our showcase environment.