What does lean manufacturing mean?
Lean manufacturing is an approach to production that aims to maximize added value and minimize waste. Processes are freed from anything unnecessary. The concept is based on the assumption that every company has processes with waste that can be eliminated through the resource-efficient use of resources, personnel and materials as well as time-efficient planning and organization.
Lean manufacturing is a sub-area of lean management. In lean management, however, the focus is not only on production, but on all company activities.
Principles and methods of lean manufacturing
How do you achieve lean manufacturing? VDI Guideline 2870 on “Holistic Production Systems” addresses this question. It provides a total of eight basic principles.
The flow principle
The flow principle pursues the goal of creating faster information and material flows by coordinating production steps and avoiding intermediate storage. You can find an example in the 5S method or the 6S method.
The pull principle
The pull principle means that production is only based on customer orders. This avoids overproduction. In practice, the pull principle is often reflected in just-in-time production (JIT).
The zero-defect principle
The name says it all: with the zero-defect principle, work steps should be carried out without errors and consequently only error-free products should be passed on to the next process step. Supporting methods can be found, for example, in Poka Yoke or SPC.
Continuous improvement processes (CIP)
Here, too, the name says it all: a continuous improvement process aims to constantly optimize production and ultimately perfect it.
Standardization
Standardized and documented work processes guarantee consistent product quality, regardless of the individual employee. Standardization can be implemented in the form of Standard Operating Procedures (SOP), for example.
Avoiding waste (Muda)
Time, money, space - in production there are usually all kinds of things that are sometimes wasted unnoticed. If these wastes can be avoided, this leads to shorter throughput times and cost savings.
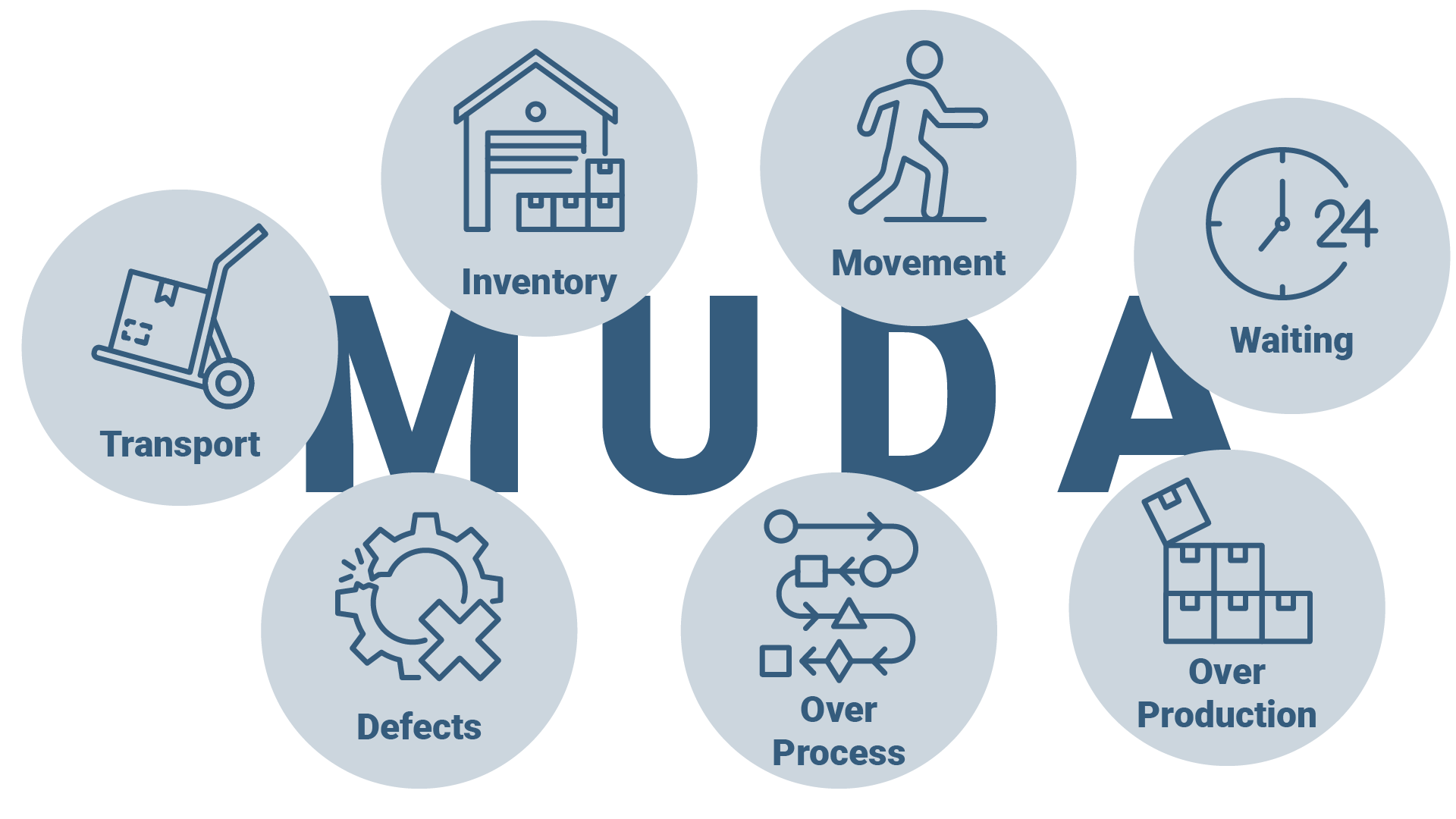
The 7 Muda - types of waste - include
- T - Transportation - unnecessary transportation
- I - Inventory - warehousing
- M - Motion - unnecessary movements
- W - Waiting - waiting times
- O - Overproduction
- O - Overengineering - suboptimal manufacturing process
- D - Defects - rejects, errors, rework
In technical jargon, this is abbreviated to TIMWOOD.
Visual management
A picture is worth a thousand words and a dashboard more than thousands of data. Information, processes and goals should therefore be presented visually. This increases transparency and makes it easier to recognize changes. Common tools for this are Andon and Kanban, for example.
Employee and goal-oriented management
You can also support lean production by focusing on your employees and the goals to be achieved. Motivate your employees to think for themselves, to avoid errors and to optimize processes, e.g. through active feedback. Also make sure that your managers work in a target-oriented manner according to specifications.
How do you establish lean manufacturing in your company?
Step 1: Sensitize your management level to lean management and lean manufacturing. If you have the support “from the top”, also train your employees so that they have an idea of what is behind the concept.
Step 2: Analyze the current situation in your company. Use standardized procedures such as process flow diagrams.
Step 3: Draw up an improvement plan together with all parties involved. In this plan, you define what is to be improved, when and with what objectives.
Step 4: Establish lean manufacturing based on the appropriate lean methods.
Step 5: Monitor your lean manufacturing using defined KPIs such as throughput time, overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) or the error rate. Draw conclusions and use them for continuous optimization.
What are the advantages of lean manufacturing?
- Increased productivity: Lean processes create space for other important processes, which in turn leads to an increase in your productivity.
- Cost savings: By eliminating waste in your production, you save time, storage space, materials, etc. And ultimately, all of this saves you money.
- Greater employee involvement: Lean manufacturing is a joint effort. You pull together with your employees and involve them in the processes more than before.
- Increased production flexibility: The leaner the process, the more flexibly you can produce. For example, if you produce in line with demand using the just-in-time method, you can react much more flexibly to requirements than if you produce to stock.
- Improved product quality: Continuous quality controls are designed to detect errors at an early stage and avoid rejects. This streamlines the production process and improves product quality.
What are the goals of lean manufacturing?
Let's summarize briefly and concisely: The aim of lean manufacturing is to eliminate waste and establish continuous improvements to optimize production processes.
In concrete terms, this means that products are manufactured continuously and without buffer times, which in turn leads to shorter throughput times.
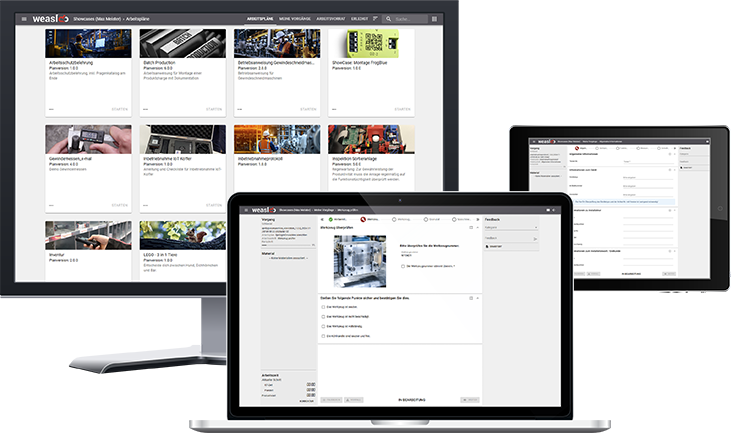
Practical support for lean manufacturing with weasl
Avoiding errors, providing standardized work instructions, establishing quality controls - these are all key disciplines of our worker guidance system weasl.
With weasl, you create important foundations for lean manufacturing and benefit from the versatility of a particularly flexible system. Experience what weasl can do - in our free showcase environment.